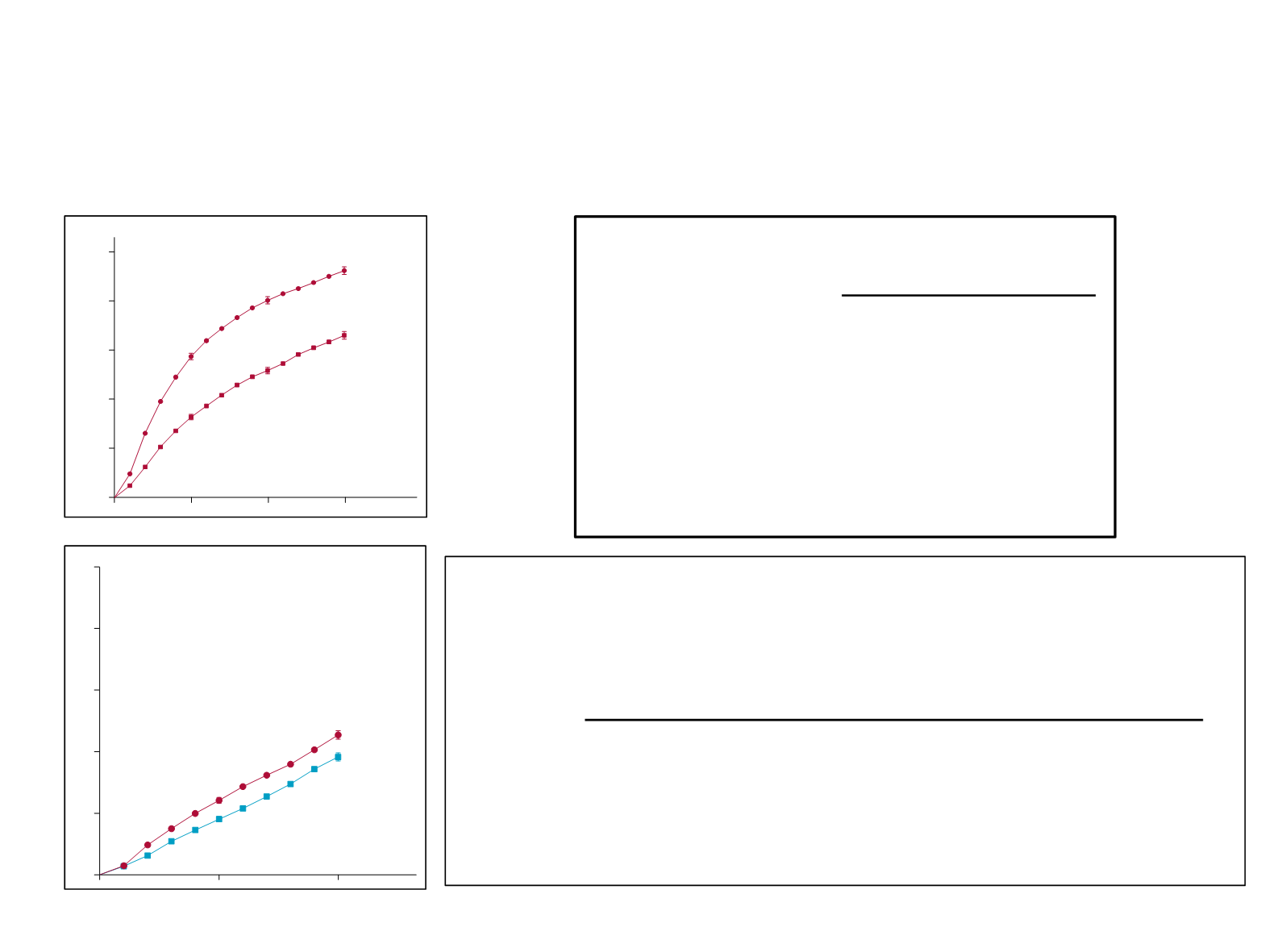
Tamoxifeno - IA
POSTMENOPAUSICAS –
5 a de IA vs 5 a de Tamoxifeno – Datos a 10 años
Reducción de riesgo
Ganancia absoluta
Recurrencia
30%
3,6% (22,7
19,!%)
Muerte x CM
15%
2,1% (14,2
12,1%)
(40% vs no tto)
TMX X 5 AÑOS VS NO TRATAMIENTO
10 a
15 a
Recu
RR
0,61
Absoluto
14,2
13,2
Muerte x CM
RR
0,7
Absoluto
7,2
9,2
CM RH+ - 5 años de TMX – resultados 15 a
EBCTCG Met -análisis
Articles
(webappendix p 4) or endometrial cancer incidence (data
not shown). There were highly significant recurrence
reductions both in the six trials with no chemotherapy
(RR0·56[0·04]) and in the14trialsof chemotherapyplus
tamoxifen versus thesamechemotherapy alone(RR0·67
[0·04]), with aslightlygreater effect of tamoxifen in those
withgreater degreesof ERpositivityinbothtrial categories
(data not shown). For patients receiving chemotherapy,
tamoxifen was of further benefit whether it started
concurrently with thechemotherapy (RR0·62 [0·06]) or
after it (RR0·71[0·05]). Theslight superiority of starting
concurrently was, however, not significant, and these
tamoxifen trials did not randomise timing. In all
regimens, tamoxifen hadasubstantial effect (figure4).
almost all those allocated treatment would have been
partially or fully treated) and by almost half during the
next 3years. During years 5–9after randomisation there
was (in all but two trials
23–26
) no difference in adjuvant
tamoxifen usebetween thetreatment andcontrol groups,
yet the r currence rate was still almost a third lower in
those originally allocated tamoxifen (RR 0·68 [0·06],
p<0·0001). Afte y ar 10, recurrence rates were similar
(RR0·97[0·10]) in thetwogroups, indicatingnolossafter
year 10of thegainsduringyears0–9.
Figure5shows15-year resultsfor recurrenceandbreast
cancer mortality in all women with ER-positive disease.
Remarkably, theyearlyrateof breast cancer mortalitywas
reduced by about a third (RR 0·70 [0·05], p<0·00001)
Figure5:
Effectsofabout 5yearsoftamoxifenonthe15-yearprobabilitiesofrecurrenceandofbreast cancermortality,forER-positivedisease
Outcomebyallocatedtreatment intrialsofabout 5yearsofadjuvant tamoxifen.Event rateratio(RR)isfromsummedlog-rank statisticsforall timep riods.Gin
(anditsSE)isabsolutedifferencebetweenendsofgraphs.ER=oestrogenreceptor.O–E=observedminusexpected, withvarianceV.
Tamoxifen
Control
Rateratio
(O–E)/V
0
5
10
15years
3·74(891/23819)
6·71(1466/21862)
0·53(SE0·03)
–343·3/535·1
2·62(454/17315)
3·46(499/14420)
0·68(SE0·06)
–82·5/217·5
2·06(220/10657)
2·11(182/8620)
0·97(SE0·10)
–3·3/93·3
1·75(88/5034)
1·76(71/4045)
0·88(SE0·16)
–4·4/35·5
Recurrencerates(%per year)andlog-rankanalyses
0
10
20
30
40
0
5
10
15years
1·79(SE0·08)
2·46(SE0·10)
0·71(SE0·05)
–84·4/244·8
2·25(SE0·11)
3·23(SE0·13)
0·66(SE0·05)
–95·8/233·2
1·54(SE0·11)
2·28(SE0·14)
0·68(SE0·08)
–38·6/99·4
1·48(SE0·16)
1·89(SE0·19)
0·88(SE0·14)
–5·7/42·6
Deathrates(%per year:totalratemin sratein women
without recurrence)andlog-rankanalyses
50
Recurrence(%;±1SE)
Breast cancermortality(%;±1SE)
Recurrence
Breast cancermortality
Years0–4
Years5–9
Years10–14
Year15+
Years0–4
Years5–9
Years10–14
Year15+
Control
46·2%
33·0%
≈5years
tamoxifen
RR0·61(95%CI0·57–0·65)
Log-rank2p<0·00001
15-yeargain13·2%(SE1·1)
Control
33·1%
23·9%
≈5years
tamoxifen
RR0·70(95%CI0·64–0·75)
Log-rank2p<0·00001
15-yeargain9·2%(SE1·0)
10645women(100%ERpositive,44%nodepositive,51%chemotherap y)
10645women
25·1%
17·9%
8·6%
11·9%
40·1%
25·9%
16·4%
28·7%
(
(
(
(
10*a* *15
Recu*
RR (
(
(
(
(
(0,6
Absoluto(
(
(14,2(
(13,
(
Muerte*x*CM*
RR (
(
(
(
(
(0,7
Absoluto (
(
(7,2 (
(9,2
(
<*45*años
(
Recu*
RR (
(
(
(
(
(0,6
(
Muerte*x*CM*
RR (
(
(
(
(
(0,7
Absoluto (
(
(7 (
(11,
Articles
Tamoxifen
Control
0
5
10
15years
2·15(SE0·19)
2·80(SE0·21)
Deathrates(%peryear:totalrateminusrateinwomen
without rcurrence)andlog-rankanalyses
0
10
20
30
40
50
Breast cancermortality(%;±1SE)
ER-positivediseaseonly:entryage<45years
Years0–4
2·63(SE0·25)
3·74(SE0·30)
Years5–9
1·29(SE0·24)
2·39(SE0·35)
Years10–14
0·98(SE0·37)
0·85(SE0·38)
Year15+
5
10
15years
2·29(139/6058)
2·91(178/6109)
Deathrates(%peryear)andlog-rankanalyses
Years0–4
2·72(116/4263)
3·89(161/4140)
Years5–9
1·52(33/2167)
2·79(55/1970)
Years10–14
1·40(10/715)
1·52(9/591)
Year15+
2614women(44%nodepositive,79%chemotherapy)
2614women
0
Anydeath(%;±1SE)
RR0·71(95%CI0·61–0·83)
Log-rank2p=0·00002
15-yeargain10·6%(SE2·2)
RR0·71(95%CI0·61–0·83)
Log-rank2p<0·00001
15-yeargain11·2%(SE2·3)
Control
35·9%
25·3%
≈5years
tamoxifen
Control
38·1%
26·8%
≈5years
tamoxifen
13·4%
10·3%
28·0%
21·0%
13·9%
11·0%
29·0%
22·0%
Cualquier((edad(
<45(a(
Cualquier(Edad(
N+(N`(
RE+/(RP+(
RE+/(RP`(
RE`/(RP+(
AI vs TMX en pacientes postmenopáusicas
Aromataseinhibitorsversustamoxifeninearlybreast
cancer:patient-levelmeta-analysisof therandomisedtrials
EarlyBr ast C cerTrali ts’CollaborativeGroup(EBCTCG)*
Summary
Background
The optimal ways of using aromatase inhibitors or tamoxifen as endocrine treatment for early breast
cancer remainsuncertain.
Methods
Weundertookmeta-analysesof individual dataon31920postmenopaus l womenwithoestrogen-receptor-
positiveearlybreast cancer in therandomisedtrialsof 5yearsof aromataseinhibitor versus5yearsof tamoxifen; of
5 yearsof aromatase inhibitor versus2–3 yearsof tamoxifen then aromatase inhibitor toyear 5; and of 2–3 years
of tamoxifen thenaromataseinhibitor toyear 5versus5yearsof tamoxifen. Primaryoutcomeswereanyrecurrence
of breast cancer, breast cancer mortality, death without recurrence, and all-cause mortality. Intention-to-treat
log-rank analyse , stratifiedbyage, nodal status, and trial, yielded aromatas inhibitor versustamoxifen first-event
rateratios(RRs).
Findings
In thecomparis n of 5 year of aromatase inhibitor versus5 yearsof tamoxifen, recurrence RRsfavoured
aromataseinhibitorssignificantlyduringyears0–1(RR0·64, 95%CI 0·52–0·78) and2–4 (RR0·80, 0·68–0·93), and
non-significantly thereafter. 10-year breast cancer mortality was lower with aromatase inhibitors than tamoxifen
5*a*de*IA*vs*5*a*de*Tamoxifeno*^10*año **
#
#
Articles
inhibitor drug, siteof first r currence, entry age, BMI,
and tumour characteristics: PR status, nodal status,
tumo di meter, tumour gr de, and HER2 status
(availablefor onlyone-thirdof patients). Therecurrence
RRs were similar with different aromatase inhibitors
(e c p<0·0001), wi h ocal recurrence, contralateral
0
5
10
0
10
20
30
40
50
A
Recurrence(%)
Recurrencerate/year(%),events/woman-yearsandlog-rankstatistics
Allocation
AI
Tamoxifen
Rateratio(95%CI)
Years0–1
1·62(157/9691)
2·41(230/9542)
0·64(0·52–0·78)
Years2–4
2·14(285/13336)
2·62(338/12906)
0·80(0·68–0·93)
Years5–9
2·33(365/15648)
2·48(372/14985)
0·92(0·79−1·06)
Year10+
3·23(20/619)
4·54(24/529)
0·72(0·39−1·30)
9885women,1791events
RR=0·80(95%CI0·73–0·88)
0
5
10
0
10
20
30
40
50
B
Breast cancermortality(%)
Deathrates(%/year: totalrateminusratein womenwithoutrecurrence)andlog-rankstatistics
Allocation
AI
Tamoxifen
Rateratio(95%CI)
Years0–1
0·52(0·39−0·66)
0·51(0·39−0·67)
0·98(0·66−1·46)
Years2–4
1·23(1·05−1·41)
1·60(1·38−1·83)
0·74(0·60−0·91)
Years5–9
1·66(1·46−1·86)
1·81(1·60−2·02)
0·90(0·76−1·07)
Year10+
1·93(0·88−2·99)
1·88(0·77−2·99)
1·01(0·45−2·33)
9885women,1066deaths
RR=0·85(95%CI0·75–0·96)
10-yeargain3·6%(95%CI1·7to5·4)
Log-rank2p<0·00001
Tamoxifen
22·7%
AI
19·1%
12·1%
9·0%
10-yeargain2·1%(95%CI0·5to3·7)
Log-rank2p=0·009
Tamoxifen
14·2%
AI
12·1%
5·8%
4·5%
age, BMI,
dal status,
R2 status
(availablef r onlyone-thirdof pati nts). Therecurrence
RRs were similar with different aromatase inhibitors
(each p<0· 01, with local recur ence, contralateral
50
B
9885women,1066deaths
RR=0·85(95%CI0·75–0·96)
EBCTCG The Lancet 2011; EBCTCG The Lancet 2015
8


